
Math that feels good
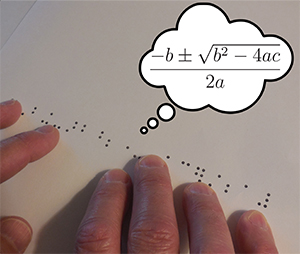
Mathematics and science Braille textbooks are expensive and require an enormous effort to produce — until now. A team of researchers has developed a method for easily creating textbooks in Braille, with an initial focus on math textbooks. The new process is made possible by a new authoring system which serves as a “universal translator” for textbook formats, combined with enhancements to the...

The Classification of Fusion Categories
Understanding and organizing the basic building blocks of mathematics and physics is one of the most natural of scientific endeavors. We do this with the elements in our periodic table, with descriptions of elementary particles, and with many mathematical structures. Perhaps the simplest example is the description of integers is products of primes. Paul Bruillard, Siu-Hung Ng, Eric C. Rowell,...

Triangle Tiling Billiards and a Cat in the Rain
Contributed by Olga Paris-Romaskevich Tiling billiards is a mathematical model for the movement of light in heterogeneous media made from homogeneous pieces. Objects in water, seen through a flat surface, do appear magnified when the eye is close to the surface. Anyone who has used a diving mask is aware of it. The reason for this effect is the Snell’s law of refraction: light refracts when...


Establishing a Theoretical Understanding of Machine Learning
Program at IAS aims to explain the why and how of algorithms with enormous power “It’s kind of like physics in its formative stages—Newton asking what makes the apple fall down,” says Sanjeev Arora, Visiting Professor in the Institute for Advanced Study’s School of Mathematics, trying to explain the current scientific excitement about machine learning. “Thousands of years went by before science...

Mathematical Optimization of Systems Impacted by Rare, High-Impact Random Events
Decision-making in systems impacted by rare, high-impact uncertain events is important and challenging due to the potential for extreme adverse effects. Mathematical optimization is a powerful tool that can help decision-makers design, plan, and operate complex systems, but planning for the possibility of such events introduces significant mathematical modeling and computational challenges. To...


Magnetic Bottles for Fusion Energy
A plasma is like a square dance gone awry. As the pace and intensity of the music (the temperature) increases, the partners (the atoms) separate into unattached dancers (electrons and ions) interacting throughout a riotous turbulent sea of independent participants (a plasma). The study of hot plasmas is central to the search for the limitless supply of energy by the nuclear fusion reaction and...


Varieties of Varieties
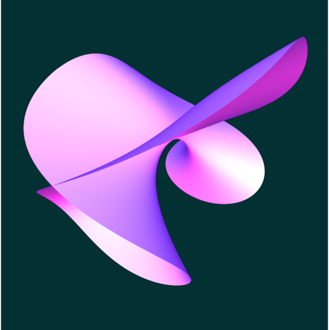
Polynomials are fundamental mathematical objects. Many basic practices in our lives are expressed through polynomials, and the same is true for the laws of science. Einstein’s famous formula expresses energy, E, in terms of a polynomial of degree 1 in m – the mass – and of degree 2 in c – the speed of light, as E = mc2. Algebraic geometry studies those geometric objects, called (algebraic)...

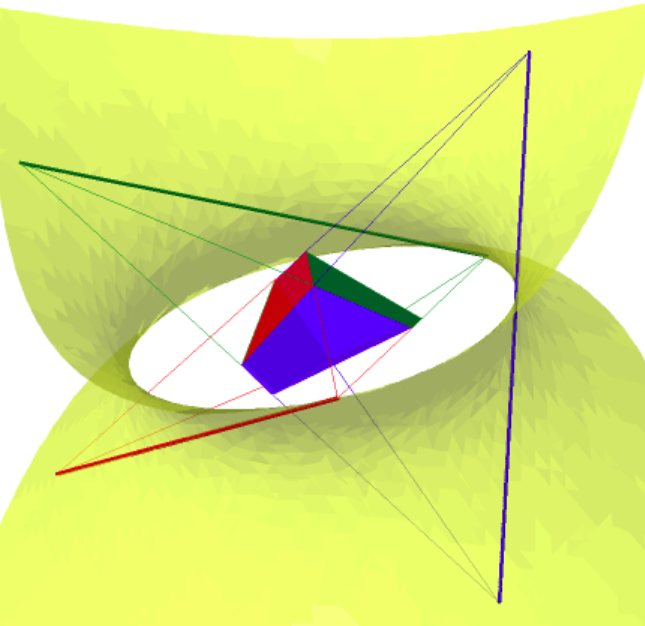
Projective geometry of Wachspress coordinates
The barycentric coordinates of a triangle were introduced by August F. Möbius in 1827. They describe a point in a triangle relative to the three vertices of the triangle. A point in the interior of a triangle splits the triangle into three smaller triangles, as seen in the first figure. The ratios of the three areas of the smaller triangles by the area of the big triangle are the barycentric...

Cutting Cakes and Splitting Rent – Combinatorics and Fair Division
How do you divide a cake fairly among several people with different preferences? How do you assign rooms and divide the rent among roommates so that no one envies the room and portion of rent paid by the other? Both of these are questions of fair-division, and mathematicians have shown that answers can be found using a combinatorial result known as Sperner’s Lemma. Sperner’s Lemma says the...

IAS Special Year 2017-2018: Analysis and Topology on Locally Symmetric Spaces
The subject of the special year was locally symmetric spaces. Examples of these highly symmetric objects are the hyperbolic geometries investigated by Bianchi in the 19th century (the first illustration (on the left) is from Bianchi’s 1893 paper) and a 6-dimensional space parameterizing all possible three-dimensional lattices up to rotation (the second illustration (on the right) shows such a...