Universality and Integrability in Random Matrix Theory and Interacting Particle Systems
This semester, participants in the Universality and Integrability in Random Matrix Theory and Interacting Particle Systems semester program studied the broad connections between random matrix theory and interacting particle systems, which can be used to model atoms or molecules, but also to find applications in areas as dissimilar as traffic flow, epidemiology, and financial markets.

Connecting Configurations
Consider a straight line in a plane with a point on it. Imagine moving the point on the line and moving the line in the plane. A parameter space can be constructed so that each point in the space represents a possible point-line configuration. Moreover, if one configuration can be turned into another by moving the point and the line just a little bit, then the corresponding points of the two configurations in the space are close. This space has a very nice and symmetric geometric shape.

African Diaspora Joint Mathematics Workshop
The African Diaspora Joint Mathematics Workshop (ADJOINT) is a yearlong program that provides opportunities for U.S. mathematicians, especially those from the African diaspora, to form collaborations with distinguished African American research leaders on topics at the forefront of mathematical and statistical research.


Fluid Dynamics
Fluid dynamics is a broad area of research that has been the subject of mathematical investigation for hundreds of years, inspired by but not limited to practical applications in biology, chemistry, physics, and engineering.


Institute for Advanced Study researcher mines polynomial patterns in dense sets
Sarah Peluse has spent the past few years looking for patterns in numbers. Specifically, she’s been looking for polynomial progressions, which involve sequences of numbers with a fixed common ratio plus a fixed value (x, x + y, x + y2), such as 3, 3 + 3, 3 + 32. Prior work had proved that once a set of numbers gets big enough, it reliably contains these polynomial progressions. But nobody knew just how big exactly.

Reduced basis approaches to speed up kinetic transport simulations
Linear kinetic transport equations play a critical role in optical tomography, radiative transfer and neutron transport. The physical and velocity/angular variables that the solution depends on are 6-dimensional, and the problem is inherently multiscale in nature. These features hamper the efficient and accurate numerical simulation of such problems. As part of ICERM’s Spring 2020 program on Model and dimension reduction in uncertain and dynamic systems, Yanlai Chen, Yingda Cheng, Fengyan Li, and Zhichao Peng joined together to work on a reduced order model approach that would allow efficient and robust simulations of linear kinetic transport equations.


Decision Making in Health and Medical Care
New models are challenging old norms for how regulatory bodies oversee the drug discovery process and approve much needed new therapies. Importantly, I-SPY 2 and now GBM AGILE, are prototypes for drug platform trials for COVID-19, Alzheimer’s Disease, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, and other diseases. Modern statistical methods, and new computational learning and decision-making tools are contributing to a hopeful future for those stricken with deadly and debilitating diseases.


Math & Racial Justice
In response to the groundswell of support for racial justice initiatives following the killing of George Floyd, a Black man, by a White police officer in Minnesota, this workshop addressed algorithmic bias; fair division, allocation, and representation; public health disparities; and racial inequities in mathematics education.


Squeezing data with the power of algorithms
Two computer scientists determine the smallest amount of data needed to estimate the mean When two fields of study collide, advances that were once all but unimaginable can be realized. At least that’s what two computer scientists showed when they applied the algorithmic tools of their field to solve the statistics problem of how to accurately guess the average value of a phenomenon from as few...

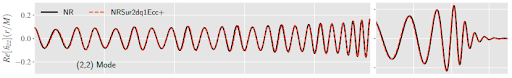
Eccentric binary black hole surrogate models for the gravitational waveform and remnant properties: comparable mass, non-spinning case
Black holes are fascinating objects! They become more so when two of them merge. Merging black holes radiate energy in the form of gravitational waves (GWs). GWs then propagate intergalactic distances to reach Earth. Ground-based detectors operated by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) and Virgo are capable of detecting such signals. Detection of GWs can help us to...