
Minimizing P-Frame Energy
Figure 1. Projections of a configuration on the unit sphere in [math]$ \mathbb{R}^6 $[/math], consisting of the coordinate axes and vertices of the inscribed hemicube; i.e., the black vertices of the cube in a black and white coloring with alternating order. The 64 total vertices of the 6-dimensional cube give 32 vertices of the hemicube; adding 12 points on the axes amounts to 44 vectors....

SAMSI Blog: Where are you Gonna go when the Volcano blow?
This article provided by Bruce Pitman, Professor in the Department of Materials Design and Innovation School of Engineering and Applied Science at the University of Buffalo. It highlights how the practice of statistics is used to mitigate risk hazards during natural disasters, such as a volcanic eruption. One of the major hazards of volcanic activity is inundation by debris flows, block and ash...

Math careers in academia
What is like to live the life of a math professor? There are many answers to this question, and they very much depend upon the nature of the mathematician’s institution. A professor at a private research university will have a different set of responsibilities and priorities to one at a liberal arts college, and different again, to someone at a large, state university. Differences also emerge...


Undergraduate Proves a Conjecture in the Theory of Water Waves
Seung Wook So, an undergraduate participant in ICERM’s Spring 2017 program on “Singularities and Waves In Incompressible Fluids,” discovered a proof of a conjecture in the theory of water waves. The question of how steep traveling water waves can become has a long history, going back at least to Stokes [Sto47]. During the ICERM program, So studied the specific question: how steep can traveling...


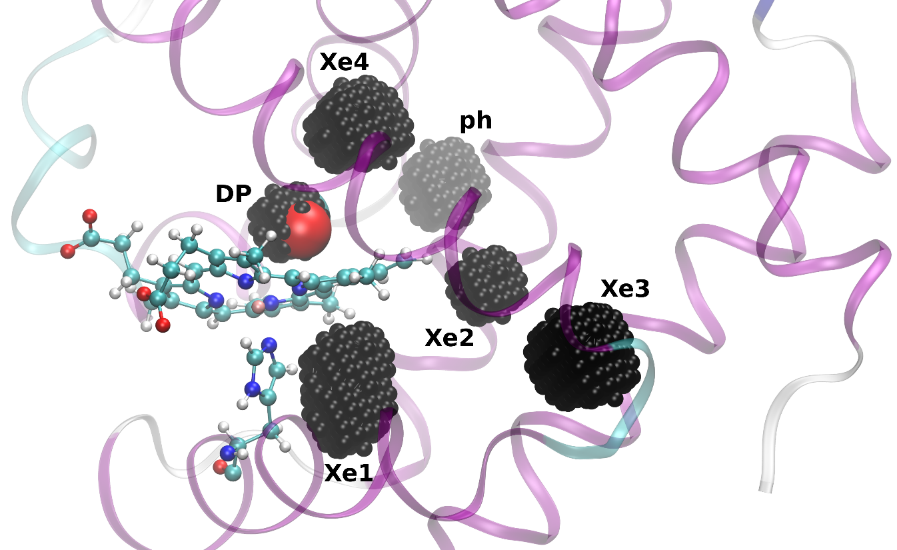
Accelerating molecular dynamics to reach unprecedented simulation times with atomistic accuracy
Molecular dynamics (MD), the numerical integration of the equations of motions of atoms and molecules, is one of the most powerful tools available to materials scientists, chemists, and biologists, because it provides a fully resolved view of the spatio-temporal evolution of materials. Because of its unparalleled predictive power, MD is extensively used to understand and optimize the properties...

Why Zebrafish (Almost) Always Have Stripes
Words by Jeff Grabmeier, Ohio State News, grabmeier.1@osu.edu One of the most remarkable things about the iconic yellow and blue stripes of zebrafish is that they reliably appear at all. Zebrafish begin life as transparent embryos, with three types of pigment cells on their skin. As they develop, the pigment cells somehow manage to organize themselves almost without fail into the stripes we all...

Data-to-Born Transform for Imaging with Waves
Imaging medium properties with waves is ubiquitous in geophysical seismic exploration, medical ultrasound diagnostics, non-destructive evaluation and testing of structures, radar and sonar surveying, etc. Most commonly, one obtains an image by probing the medium of interest with wave pulses emitted and recorded by an array of sensors. Typically, the image is based on the reflectivity, a...

SAMSI Research Develops Improved Estimates of Ocean Heat Content Changes
Ongoing research at the Statistical and Applied Mathematical Sciences Institute (SAMSI) has produced improved estimates of ocean heat content leading to a better understanding of which regions of the ocean are warming up and which ones are cooling down. This animation shows monthly vertically integrated ocean heat content anomalies for 2007-2016 using data from Argo profiling floats from the...

The 2016-17 IAS program on Homological Mirror Symmetry (HMS)
Homological Mirror Symmetry Image by Ailsa Keating, used with permission The subject of the program in context HMS started with Kontsevich’s 1994 ICM address. By now, it is a mature area of mathematics in its own right, but still one that can be approached from many different directions, which interact fruitfully even when they remain formally (in the theorem-and-proof sense) independent. More...

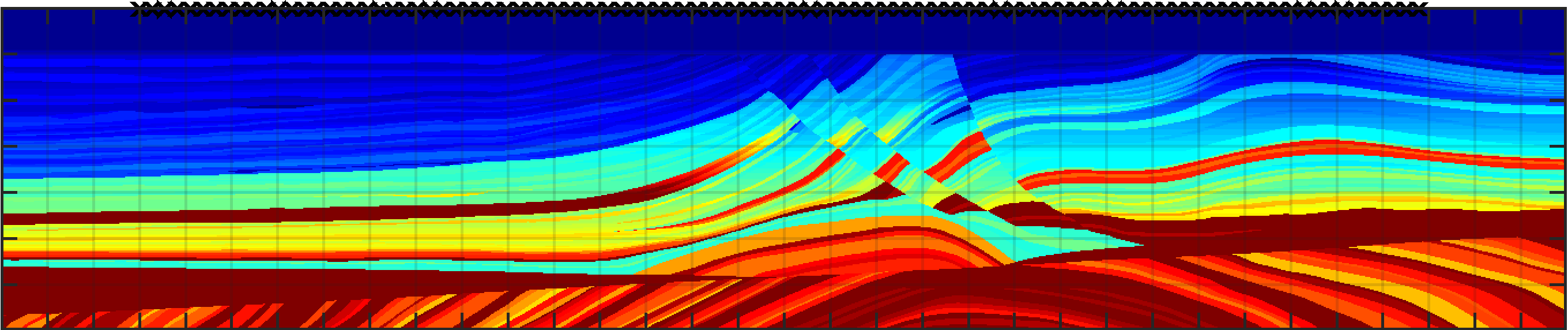
A Few Self-driving Cars Can Dramatically Improve Traffic Flow
The presence of just a few autonomous vehicles can eliminate the stop-and-go driving of the human drivers in traffic. Under normal circumstances, human drivers naturally create stop-and-go traffic, even in the absence of bottlenecks, lane changes, merges or other disruptions. A small percentage of autonomous vehicles can have a significant impact on the road, eliminating waves and reducing the...